Our Work
Safe Chemicals and Facilities
Learn about our collaborative teams and campaigns.
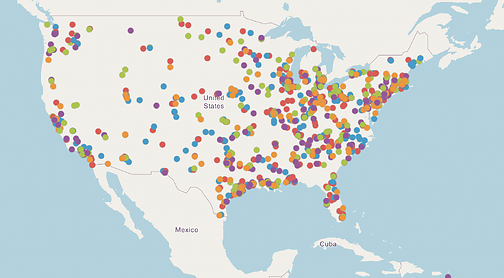
Explore the data
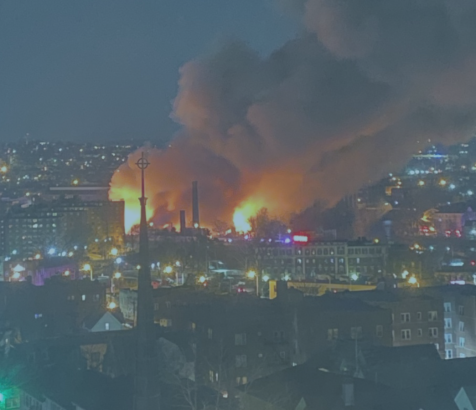
Chemical fires, explosions and toxic releases occur every other day in the U.S.
Data points are uploaded weekly by the Coalition to Prevent Chemical Disasters.
Watch the video: Life at the Fenceline
There are over 12,000 extremely hazardous chemical facilities across the nation, disproportionately located in communities of color.
Related News
October 9, 2025
Trump Is Using the Shutdown to Supercharge His War on Equity
As the federal government shutdown stretches into its second week, President Donald Trump is targeting nearly $30 billion in cuts to federal funding almost exclusively to Democratic states and cities. The impact of the cuts to public transit, energy projects, and fundamental civil rights programs could carry far-reaching harms across the nation and the economy. The cuts are the next step in the implementation of executive orders issued by Trump that strive to eradicate policies that advance racial and gender equity, tackle the climate crisis, and threaten the fossil fuel industry. "When the Biden-Harris administration came in, they did not just create plans in a vacuum, they went and listened to people in the community” to learn what projects were needed, “and financing flowed from those discussions,” Michele Roberts of the Environmental Justice Health Alliance. The programs included projects to address historic and ongoing environmental racism and injustices, and the disproportionate health and economic burdens in Black and Brown communities that followed.
September 18, 2025
Chemical Incident Tracker updated after EPA deletes data
The Coalition to Prevent Chemical Disasters published updates to its open-access chemical disaster tracking tool today that allow users to see how close they live to highly hazardous facilities covered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Risk Management Program (RMP). The Chemical Incident Tracker continues to allow users to search for chemical releases, fires and explosions that have been reported in the media since January 2021, using an interactive map. The tracker is updated with new incidents weekly.
Read MoreSeptember 9, 2025
Polluter free passes show Trump Administration’s indifference to community health
Exposure to chemical plant pollution can shorten lives and contribute to many health problems. Last year, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finally took action to reduce emissions of cancer-causing toxics like ethylene oxide and chloroprene from chemical plants, and developmentally-toxic mercury and heavy metals from coal plants. President Trump’s proclamations give over 150 facilities (52 chemical plants, 39 sterilizers and 68 of the country’s dirtiest coal plants) a free pass to ignore these pollution-reducing rules that would otherwise protect lives and health.
Read MoreGutting chemical safety board endangers millions of Americans, groups warn Congress
A coalition of environmental, labor and public safety groups are calling on US lawmakers to reject the Trump administration’s move to eliminate a federal unit that investigates chemical accidents, citing risks to more than 170 million people who lives in zones at risk for such events. In a July 17 letter to leaders in the US House and Senate, the coalition said the White House plan to eliminate the US Chemical Safety and Hazard Investigation Board (CSB) comes at a time when there have been at least 105 “serious chemical disasters” reported so far this year.
Read MoreAugust 28, 2025
Environmental Groups Sue EPA Demanding Protections from Hazardous Chemicals
A coalition led by environmental justice organizations filed a suit against the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency today for refusing to issue long-overdue rules to prevent hazardous-substance discharges that threaten public health and contaminate waterways. Across the United States, more than 100,000 facilities make, store, or use hundreds of hazardous chemicals linked to reproductive, developmental, and neurological harm – including benzene, hydrogen sulfide, sulfuric acid, hydrogen cyanide, and hydrochloric acid. “For generations environmental justice communities have lived next to some of the most hazardous facilities in the country that threaten the bodies of water our families rely on to survive. Now more than ever we must prioritize creating safe and healthy places where all of our children can thrive and grow.” said Michele Roberts, National Coordinator of the Environmental Justice Health Alliance for Chemical Policy Reform. “The EPA’s do-nothing approach leaves us one incident away from a catastrophe.”
Read More
August 13, 2025
Before A Steel Plant Exploded, Trump’s EPA Hid Risks From The Public
he U.S. Steel plant where two workers were killed and 10 injured in an explosion on Monday had a history of chemical accidents — but it was one of hundreds of high-risk chemical facilities that were recently hidden from the public after demands from the chemical industry. The Trump administration, at the behest of the powerful chemical lobby, has been working to gut oversight of so-called Risk Management Program facilities, chemical plants that are considered at the highest risk of deadly explosions. In April, two months after an explicit request from industry, Trump’s Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) scrubbed a tracking tool listing such facilities from its website. “This isn’t U.S. Steel Clairton Coke Works’ first incident,” Maya Nye, the federal policy director of Coming Clean, a chemical watchdog group, told The Lever. “Any time the same facility has repeated disasters, that’s a regulatory failure.”
Read MoreAugust 5, 2025
Trump gives Louisville plant more time to address pollution. Homes sit 500 feet away
Bakelite Synthetics, the only major source of formaldehyde emissions in Jefferson County, will have more time to comply with Biden-era pollution control requirements following a Trump proclamation. The plant neighbors the Riverside Gardens community, where residents have raised concerns about chemical emissions and other hazards in the past. "This would be the perfect time for this city to strengthen that permit in an effort to reduce our exposure to any of the chemicals coming from Bakelite," Eboni Cochran, a longtime environmental justice advocate with Rubbertown Emergency ACTion, or REACT, said in a text message. "There are solutions," Cochran said. "The city just needs to have enough will and courage to protect its residents."
Read MoreJuly 17, 2025
Environmental Health, Fenceline and Labor Organizations Call for Preservation of Chemical Safety Board
Today, Coming Clean, the Environmental Justice Health Alliance, and other members of the Coalition to Prevent Chemical Disasters sent a letter urging members of Congress to oppose White House proposal to eliminate the U.S. Chemical Safety and Hazard Investigation Board (CSB). The CSB is an independent nonregulatory federal agency that Congress created pursuant to federal law after deadly chemical disasters in Bhopal, India and Institute, West Virginia. It is the only federal agency charged with investigating the root causes of industrial chemical disasters; issuing reports to Congress, EPA, and OSHA; and making recommendations to prevent future disasters. This year alone, there have already been over one hundred chemical incidents in the U.S
Read More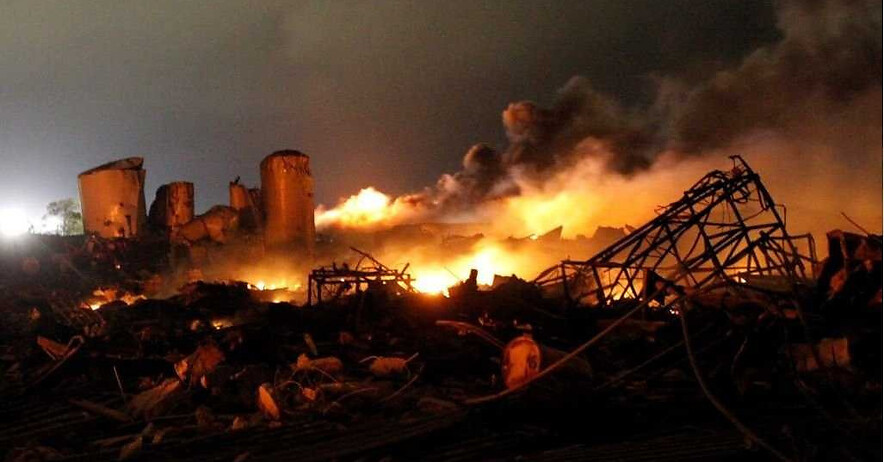
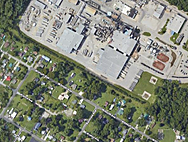
2013 Explosion and Chemical Disaster in West, Texas
Our Work Share this page: |
The Campaign for Healthier Solutions Farmworker Health and Justice Team Chemical Disaster Prevention Program |
Subscribe to our |
© 2025 Coming Clean Inc. | Coming Clean, Inc., 28 Vernon Street, Suite 434, Brattleboro, VT 05301 • (802) 251-0203